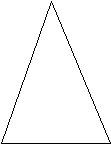
 A
A
1) Using a ruler measure AB and AC. What do you notice?
This is an example of an triangle.
2) Measure angle ABC and ACB. What do you notice?
Therefore, if a triangle has congruent sides, the angles
opposite must be .
B C
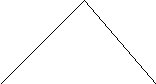 D 3) Measure angle D . Measure angle E
D 3) Measure angle D . Measure angle E
Measure angle DFG.
4) Make a conclusion regarding the relationship between
angles D and E and F.
E F G
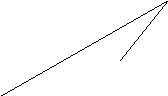 H 5) Measure sides HI, HJ, and IJ.
H 5) Measure sides HI, HJ, and IJ.
6) Measure angles H, I and J.

J 7) What type of triangle is HIJ?
I 8) If a triangle has sides that are unequal then the angles are
.
In triangle ABC below, label the following:
a) Vertex b) Sides c) 1 interior angle d) exterior angle e) altitude
e) median
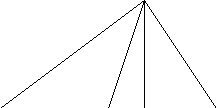 B
B
A
E D C F
Fill in: The sum of any two sides of a triangle must be the 3rd side.
Examples:
1) Find the measure of angle FGH.
F
H E
G
2) If the ratio of the degree measures of a triangle are 1: 3: 5, what is the degree of the measure of the smallest angle?
3) LMN and LNO below are isosceles triangles with the measure of angle MLN = 55 and the measure of angle LON equal to 60. If LN = LM and LN = NO, what is the measure of angle MNO?
 M
M
 N L
N L
O
Back to top
 A
A
 D 3) Measure angle D . Measure angle E
D 3) Measure angle D . Measure angle E
 H 5) Measure sides HI, HJ, and IJ.
H 5) Measure sides HI, HJ, and IJ.
 B
B
 M
M
 N L
N L