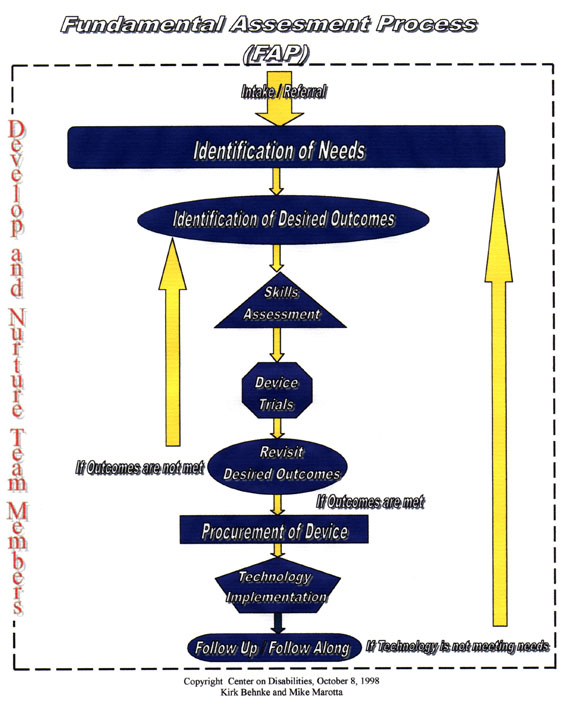
The steps included in the Fundamental Assessment Process (FAP) are:
| · Step 1: Intake / Referral | ||
| · Step 2: Identification of Needs | ||
| · Step 3: Identification of Desired Outcomes | ||
| · Step 4: Develop and Nurture Team Members |
| o | This step is on going throughout the process | |
| · Step 5: Skills Assessment | ||
| · Step 6: Device Trials | ||
| · Step 7: Revisit Desired Outcomes |
| o | If outcomes are met, go to Step 8 | |
| o | If outcomes are not met, go back to Step 3 | |
| · Step 8: Procurement of Device | ||
| · Step 9: Technology Implementation | ||
| · Step 10: Follow Up / Follow Along |
| o | If the technology is not meeting needs, go back to Step 2. | |